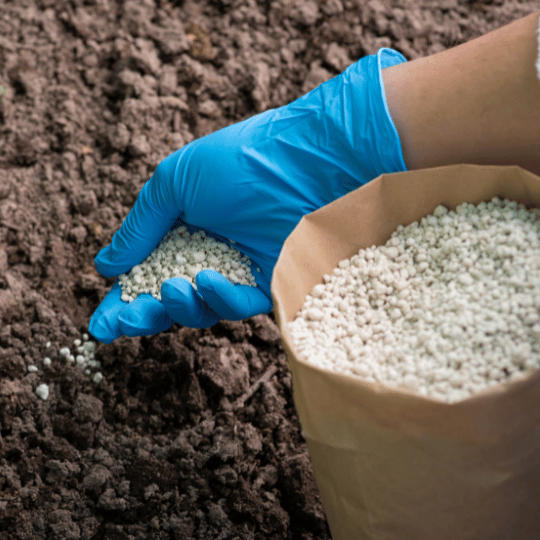

| Form | Available in solid (granular, powdered) and liquid forms |
| Color | Varies; solid fertilizers can be brown, gray, white, or green, while liquid fertilizers are often clear or colored |
| Odor | May have a slight chemical or ammonia-like odor; some organic fertilizers have a natural earthy smell |
| Density | Varies by type; granular fertilizers typically range from 0.8 to 1.5 g/cm³ |
| pH Level | Ranges from acidic to alkaline, depending on the composition; typical ranges are between 6 to 8 |
| Solubility | Water-soluble fertilizers dissolve in water, while others may be less soluble or slow-release |
| Nutrient Composition | Typically includes macronutrients (N-P-K: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) and micronutrients (Calcium, Magnesium, Iron, etc.) |
| Application Rate | Varies based on crop type and soil conditions; generally specified on the packaging |
| Granule Size | Varies from fine powders (less than 1 mm) to coarse granules (up to 5 mm or more) |
| Moisture Content | Should be low (usually less than 5%); high moisture can lead to clumping and reduced effectiveness |
| Compatibility | Some fertilizers can be mixed (tank mixing) while others may react negatively; compatibility should be checked |
| Storage Conditions | Store in cool, dry places away from moisture and direct sunlight; avoid stacking heavy bags on top of lighter ones |
| Shelf Life | Generally long; 1-3 years for most chemical fertilizers, longer for properly stored organic fertilizers |
| Environmental Impact | Overuse can lead to nutrient runoff, water pollution, and soil degradation; responsible application is essential |
| Regulatory Standards | Must comply with local agricultural regulations and safety standards; labeling requirements are mandated |
| Function | Enhances soil fertility, promotes plant growth, and increases crop yield |