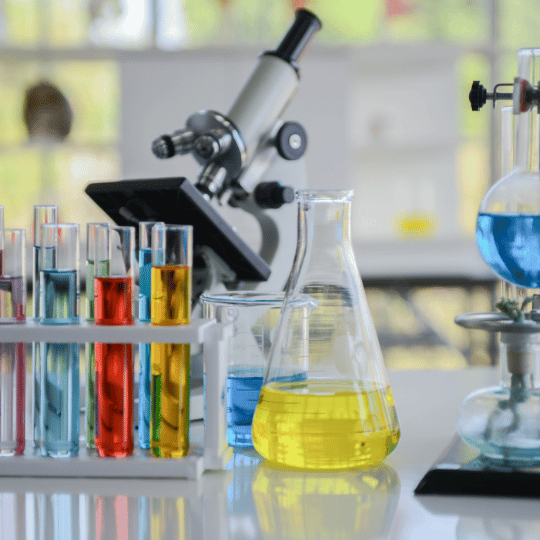

| Form | Available in liquid, powder, granules, and emulsifiable concentrate forms |
| Color | Varies; liquids are often clear or light yellow, powders may be white or colored depending on the formulation |
| Odor | Chemical or sulfur-like odor; varies based on the type of agrochemical |
| Density | Varies by formulation; liquid forms typically have a density between 0.9 to 1.3 g/cm³ |
| pH Level | Ranges from neutral to slightly acidic or alkaline, depending on the chemical composition |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (for herbicides, pesticides); some forms are oil-based and emulsifiable |
| Viscosity | Low to medium viscosity for liquid formulations, free-flowing for granular and powder forms |
| Boiling/Freezing Point | Varies depending on the active ingredient; usually stable under typical agricultural conditions |
| Active Ingredients | Includes synthetic chemicals or natural substances like insecticides, herbicides, fungicides, and fertilizers |
| Toxicity | Varies; some agrochemicals can be toxic to humans and animals if ingested or improperly handled |
| Application Methods | Spraying (liquids), spreading (granules), or soil mixing depending on the form and purpose |
| Shelf Life | Typically 1-3 years when stored under appropriate conditions |
| Packaging | Packed in plastic or metal containers, bags, or drums; sizes vary from small bottles (1 liter) to bulk quantities (50 liters or more) |
| Environmental Impact | Can cause pollution if overused or misapplied; some agrochemicals are biodegradable, while others may persist in soil or water systems |
| Compatibility | Some agrochemicals are compatible with others (tank mixing), while certain combinations may cause chemical reactions |
| Storage Conditions | Store in cool, dry, and well-ventilated areas; keep away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture |
| Regulatory Standards | Must meet local and international agricultural safety standards like FAO, WHO, and national regulatory bodies |